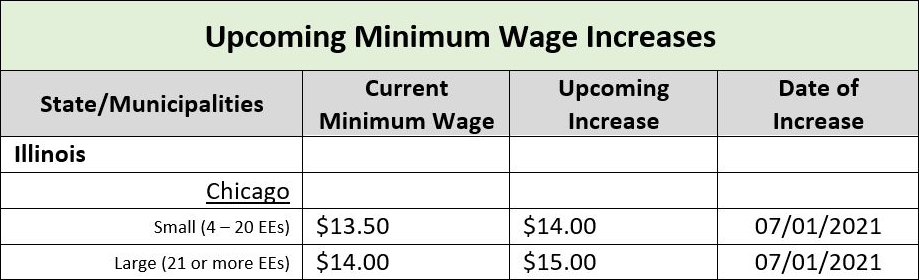
The current federal minimum wage rate is $7.25 per hour. However, many states have adopted minimum wage rates higher than the federal rate. When the state rate and the federal rate are different, employers must pay their employees the higher rate.
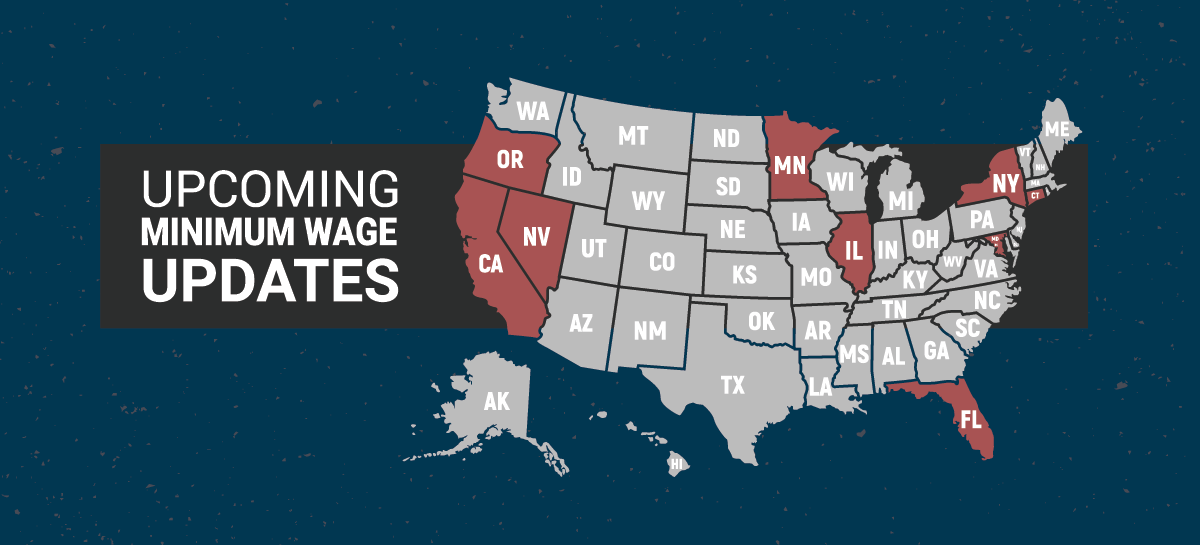
Click the image below or this link for a PDF with the full list of states that have upcoming increases, including: California, Connecticut, Florida, Illinois, Maryland, Minnesota, Nevada, New York, Oregon, and Washington DC.